Traceability in custom meat processing ensures every step of an animal’s journey – from origin to final packaging – is tracked with precision. It’s vital for safety, quality, and trust. Customers want assurance that the meat they receive comes exclusively from their own livestock, and traceability systems make this possible.
Key points:
- Safety: Quickly address contamination issues and minimize risks.
- Quality Control: Maintain consistent standards by monitoring every stage of processing.
- Consumer Confidence: Offer transparency about the meat’s origin and handling.
Wild Country Meats demonstrates how robust traceability practices – like tagging, detailed labeling, and USDA compliance – create accountability and reliability in custom meat processing. Their system ensures customers get exactly what they expect: meat sourced solely from their animals.

Traceability isn’t just about regulation; it’s about delivering safe, high-quality products while meeting the growing demand for transparency in food production.
How Traceability Improves Meat Quality and Safety
Food Safety Through Traceability
Traceability systems play a key role in protecting consumers from foodborne illnesses by making it easier to quickly identify and remove contaminated products from the market. When safety concerns arise, processors can trace the issue back to its source and isolate affected batches, minimizing the risk of widespread contamination.

Under the FDA’s Food Safety Modernization Act, regulators can demand traceability data – such as electronic, sortable spreadsheets – within 24 hours during outbreaks, recalls, or other public health emergencies. Today’s systems use IoT sensors and AI to monitor the supply chain in real time, identifying problems like temperature changes, contamination risks, or processing errors before they become major threats. This kind of proactive tracking not only helps prevent outbreaks but also lays the groundwork for consistent quality control.
"The use of traceability systems is becoming increasingly important for ensuring food safety and quality. Regulators are working closely with industry stakeholders to develop and implement effective traceability systems." – Dr. John Smith, Food Safety Expert
Traceability has the potential to cut the risk of foodborne illnesses by as much as 90%. By maintaining detailed records at every stage – from farming and processing to storage and shipping – companies can conduct targeted recalls, removing only the affected products rather than entire product lines.
But it’s not just about safety. Traceability also ensures that quality standards are met consistently throughout the supply chain.
Consistent Meat Quality Standards
Traceability systems establish a clear framework for maintaining high-quality standards across every step of meat processing. Detailed tracking – from the moment meat arrives at a facility to the final packaging – helps identify and fix quality issues more effectively.

Systems that log Critical Tracking Events (CTEs) and Key Data Elements (KDEs) create a secure, detailed record of a product’s journey. These records allow processors to confirm that customer-specific requirements – such as exact aging times, cutting instructions, or packaging preferences – are met consistently and accurately.
Building Consumer Trust
As concerns about food safety and quality grow, consumers increasingly expect transparency about the origins of their meat. Traceability provides the verified information they want, building confidence in the food they purchase. Shoppers today care about where their meat comes from, how the animals were raised, and what methods were used during processing. With robust traceability systems, companies can provide this information in a reliable, accessible way.

The 2013 horsemeat scandal – where horsemeat was falsely labeled as beef and sold across several countries – exposed significant weaknesses in supply chains and underscored the importance of traceability in preventing food fraud and mislabeling. Since then, major retailers have adopted blockchain-based traceability systems. For instance, Walmart and Carrefour use IBM’s "Food Trust" platform, built on Hyperledger Fabric technology, to track pork and poultry.
For custom meat processors, traceability ensures that customers receive meat sourced exclusively from their own animals, fostering trust and loyalty.
Traceability Benefits by Stakeholder
Traceability delivers distinct advantages to every stakeholder involved in the supply chain.
| Stakeholder | Primary Benefits | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Processors | Risk reduction and efficiency | Faster recalls, lower liability, better quality control, and regulatory compliance |
| Consumers | Safety and transparency | Verified product authenticity, clear origin details, and confidence in safety |
| Regulators | Improved oversight and rapid response | Access to data within 24 hours, detailed audit trails, and better public health protections |
Beyond safety, traceability offers operational benefits to processors, such as better inventory management, less waste, and happier customers. Consumers gain peace of mind knowing their meat is safe and authentic. Regulators, meanwhile, can focus on preventing problems rather than reacting to them. Altogether, traceability creates a cycle of improvement that benefits everyone involved.
How Traceability is Used in Beef Cattle Processing
Traceability Systems, Tools, and Standards in Meat Processing
In the meat processing industry, maintaining consumer trust and ensuring product safety are top priorities. To achieve this, processors use advanced traceability systems that follow products throughout the supply chain.
Tracking and Documentation Methods
To keep track of products from farm to table, meat processors rely on a combination of tools and methods. It all starts with animal tagging, where ear tags containing unique identification numbers are assigned to livestock. These tags, often enhanced with RFID technology, allow for quick and accurate data collection, minimizing human error.

Once animals reach the processing facility, barcoding systems take over. Each carcass is assigned a unique barcode tied to detailed records, including the source farm, arrival date, processing details, and customer information. Handheld scanners are used to update the status of each product in real time as it moves through the facility.

To add another layer of traceability, processors use lot codes. These codes group products based on processing dates, facilities, and batch numbers. For instance, a lot code like "WCM082525A" might represent Wild Country Meats, processed on August 25, 2025, batch A.
Digital inventory management systems centralize all this data in cloud-based platforms. These systems generate reports, send alerts when products reach specific aging milestones, and maintain audit trails. Workers can access this information instantly via tablets or smartphones, ensuring accuracy even during busy times.

While paper-based systems are still used as backups, digital solutions are preferred for their speed, accuracy, and data analysis capabilities. Together, these methods form the backbone of compliance with Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) standards, ensuring every critical control point is closely monitored.
HACCP Traceability and Compliance
HACCP systems are essential for food safety in meat processing. They identify hazards at each stage of production and establish critical control points to prevent contamination. These systems require detailed documentation, such as temperature logs during refrigerated storage, pH readings during curing, and timestamps for each processing stage. This data helps facilities demonstrate compliance and quickly address any safety concerns.

To maintain accuracy, verification procedures are regularly conducted. These include calibrating equipment, validating critical limits, and auditing documentation practices. Records from these reviews must be kept for at least two years, with longer retention periods required for specific products.
By integrating traceability with HACCP systems, processors create a comprehensive safety framework. If an issue arises at a critical control point, traceability systems can pinpoint the affected products, allowing for targeted corrective actions instead of widespread recalls.
New Technologies in Traceability
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing traceability in meat processing:
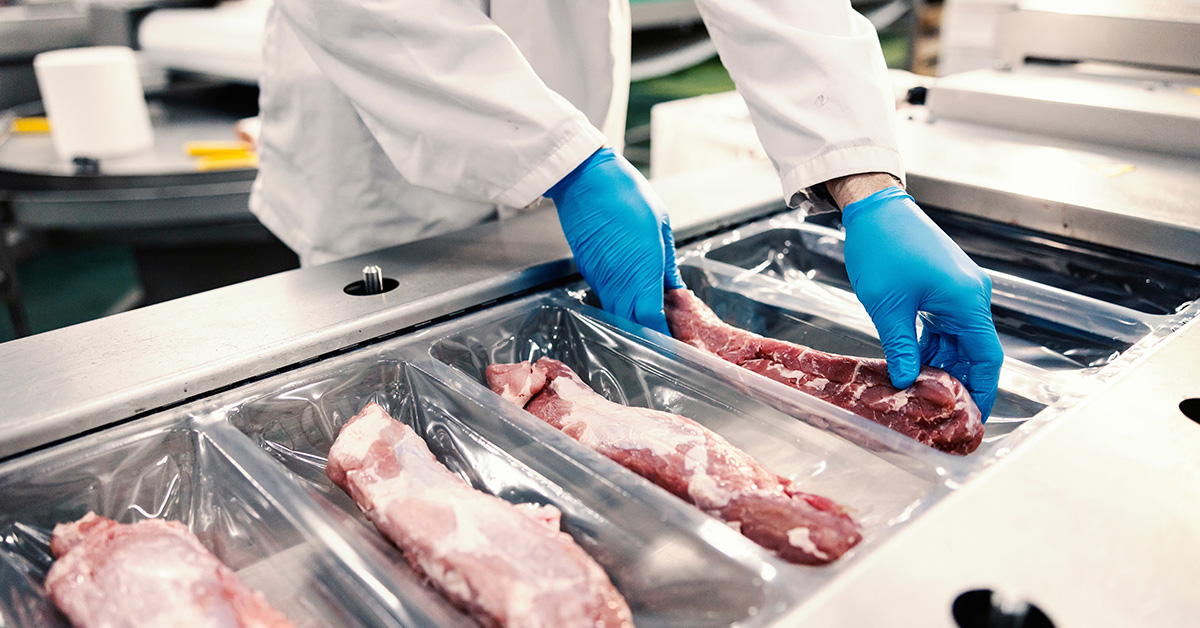

- Blockchain technology creates tamper-proof records. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain ensures that once data is entered, it cannot be altered without detection. Some processors use blockchain to provide customers with detailed product histories via QR codes, offering transparency about farm origins, processing dates, and certifications.
- IoT sensors monitor conditions across the supply chain, tracking refrigerated transport, humidity levels in aging rooms, and detecting unusual activity that could indicate tampering. These sensors provide a level of environmental monitoring that goes beyond traditional critical control points.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) analyzes traceability data to predict and resolve potential problems. AI can flag temperature fluctuations, identify delays that might impact quality, and even detect patterns linking specific suppliers to quality issues. Over time, machine learning improves the system’s accuracy.
- Mobile applications allow workers to update product statuses, scan barcodes, and capture photos using smartphones or tablets. This real-time data entry reduces errors and ensures that teams have instant access to critical information.
These innovations not only streamline operations but also help meet stringent U.S. regulatory standards.
U.S. Regulatory Standards
U.S. meat processors must comply with a range of regulations to ensure traceability and safety:

- The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) requires facilities to maintain records for Critical Tracking Events and Key Data Elements. While FSMA’s Traceability Rule primarily focuses on high-risk foods like fresh produce, many meat processors adopt similar practices to prepare for potential future requirements.
- USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) regulations mandate detailed record-keeping, including supplier verification, processing logs, and shipping documentation. Labels must include establishment numbers, inspection legends, and handling instructions. FSIS inspectors frequently review these records during inspections or investigations.
- State regulations may impose additional requirements, such as documentation for locally sourced products or enhanced traceability for direct-to-consumer sales. Processors must understand and adhere to the rules in every state where they operate.
- The FDA’s Food Code provides traceability guidelines for retail and foodservice establishments, ensuring that information flows through the entire supply chain to the end consumer. This end-to-end transparency benefits everyone involved, from processors to customers.
These systems and standards work together to ensure that meat products are safe, traceable, and compliant with both federal and state regulations. By leveraging both traditional methods and cutting-edge technologies, the industry continues to build trust and accountability.
Traceability Practices at Wild Country Meats
Wild Country Meats has built a reputation for transparency by implementing a thorough traceability system in its custom meat processing operations. From the moment an animal is dropped off to when the final product is picked up, every step is carefully tracked and documented. This process ensures customers know exactly where their meat comes from.
Animal Tagging and Inventory Management
The traceability journey begins as soon as animals arrive at the facility. Employees on the slaughter floor and dock personally tag each animal or wild game with a unique number. This tag follows the animal through every stage – holding pens or dock, kill chute, holding cooler, cutting table, and finally, the freezer.
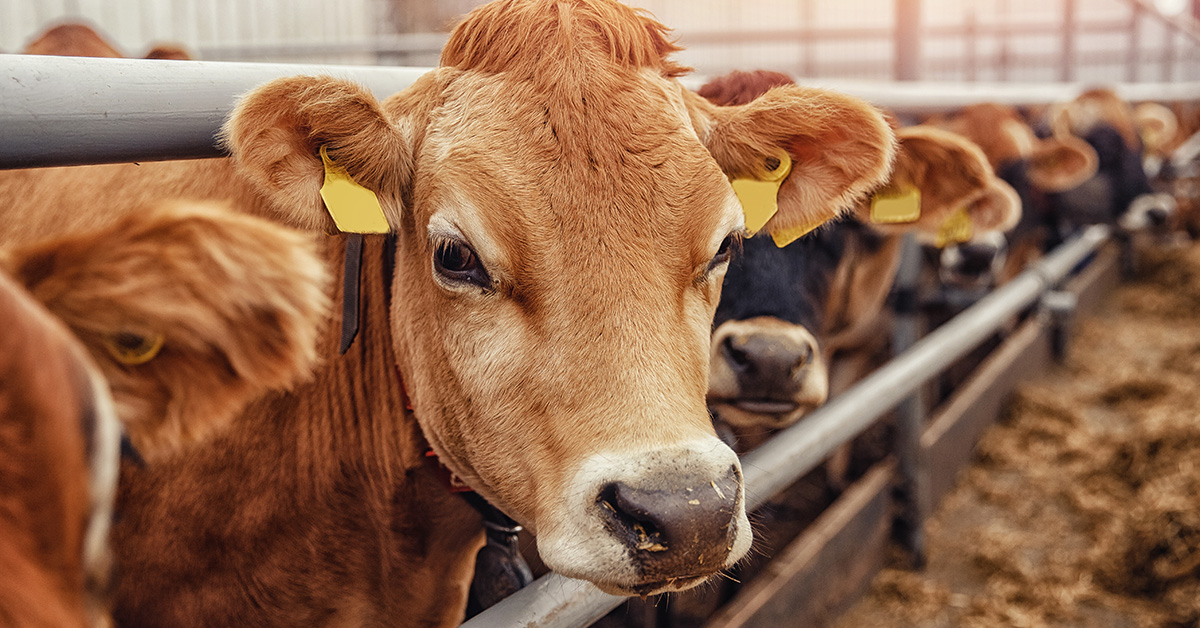

After slaughter, carcasses are immediately tagged for dry aging. To maintain purity, only one side of a carcass is processed at a time, and each animal’s meat is ground individually.
Custom Labeling and Documentation
Wild Country Meats goes the extra mile with detailed labeling and photographic documentation for every order. Each product is clearly labeled to trace its origin, and customers receive an itemized inventory report at pickup or delivery.
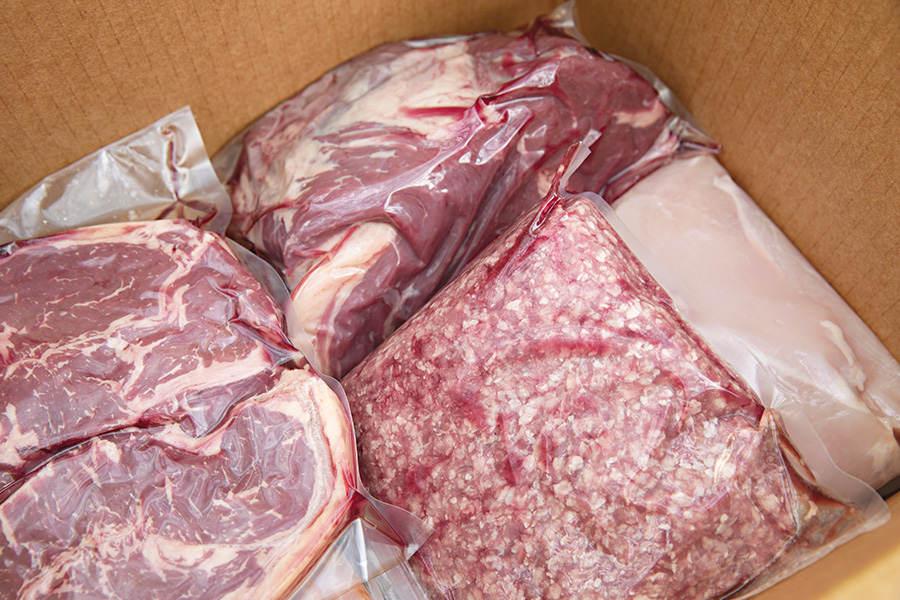

This report provides a complete breakdown of the yield from their animal, ensuring nothing is left unaccounted for. These practices not only enhance transparency but also build trust with customers.
Transparency in Custom Processing Orders
The company’s commitment to accuracy and openness is evident in their promise: the meat you receive is exclusively from the animal you brought in for processing in Oklahoma. Through a combination of tags, photos, and detailed labeling, Wild Country Meats ensures every product is tracked meticulously. Customers are provided with an inventory report that lists all meat cuts when they pick up or receive their order.
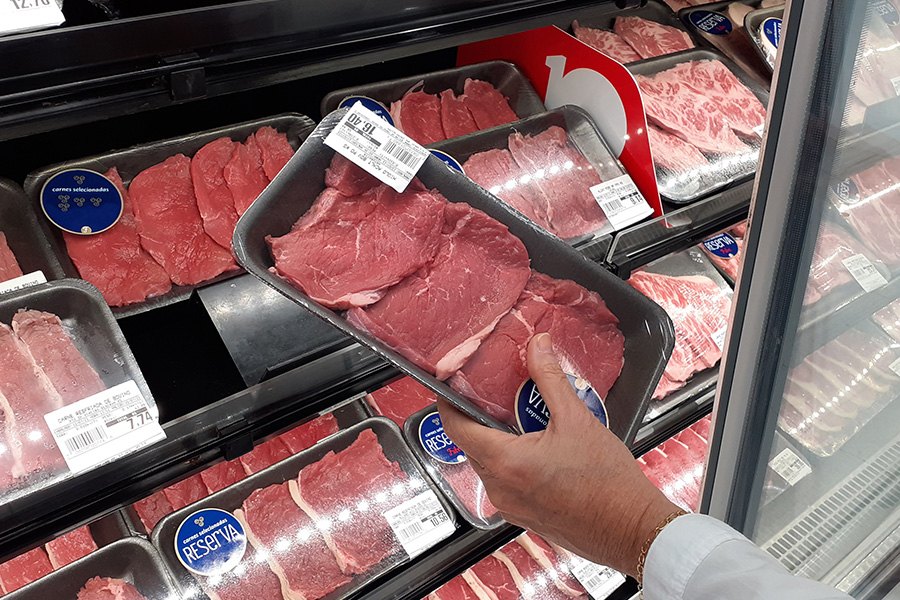

"We track your product every step of the way with tags, photos and detailed labeling and give you an itemized inventory report showing all meat cuts on pickup or delivery."
This robust traceability system not only enhances food safety but also allows for quick resolution of any quality concerns. By integrating personal tagging, photographic records, detailed labeling, and comprehensive reporting, Wild Country Meats has earned a reputation for reliability and accountability in the custom meat processing industry.
sbb-itb-5ae85c5
How to Choose Traceable Meat Sources
Choosing traceable meat involves more than just trusting a label – it’s about digging into the details to ensure the meat’s origin is clear and meets safety standards. By asking the right questions and reviewing documentation, you can make informed choices that align with your expectations for transparency.
How Consumers Can Verify Traceability
When buying meat, documentation is your best friend. Look for labels that clearly outline the animal’s origin, the processing date, and the tracking method used. To dive deeper, consider asking questions like:

- Where was the animal raised?
- Is there documentation proving its origin?
- What tracking system was used?
- Is there an itemized breakdown of the inventory?
Certifications are another layer of assurance. Confirm that processors meet federal traceability regulations to add credibility and accountability to your purchase.
How Producers Can Improve Traceability
For producers, meeting consumer expectations for traceability requires a commitment to thorough tracking systems. Every stage of production must be documented to uphold the integrity of the food chain. This approach not only ensures compliance with regulations but also helps identify safety concerns quickly and prevents food fraud.

Start by implementing a detailed documentation process. Record everything – from the animal’s origin and processing dates to storage conditions and distribution details. Use tagging systems to assign unique identifiers to animals or batches, making it easier to trace them through the supply chain. Training your team to prioritize accurate record-keeping and consistent procedures is equally important. Additionally, consider going beyond basic compliance by opting into voluntary certification programs. These certifications can address specific consumer demands for quality and transparency while doubling as effective marketing tools.
Using Wild Country Meats’ Traceability System
Wild Country Meats takes traceability to the next level with a transparent process designed for custom meat processing. They ensure that the meat you receive comes exclusively from the animal you brought in. Upon pickup or delivery, they provide an itemized inventory report detailing every cut of meat from your animal. Reviewing this report ensures everything is accounted for and meets your expectations.

Customers have shown their trust in this system, reflected in Wild Country Meats’ high rating of 4.6 out of 5. For added assurance, USDA-inspected processing options are available, offering extra documentation and oversight to meet federal standards. This comprehensive approach reinforces the industry’s broader commitment to quality and accountability.
Conclusion: Why Traceability Matters in Custom Meat Processing
Traceability plays a critical role in custom meat processing by helping processors manage recalls efficiently, maintain consistent product quality, and earn consumer trust through verified transparency.
It goes beyond simply meeting regulatory requirements. When issues arise, traceability allows processors to quickly pinpoint and isolate affected products, all while adhering to quality standards through thorough documentation and monitoring.
By integrating modern technology with traditional tracking methods, processors can surpass compliance standards and meet the growing demand for transparency. Tools like HACCP protocols, detailed labeling, and digital inventory systems provide the clarity and accountability that today’s consumers expect.
FAQs
How does traceability build consumer trust in custom meat processing?
Traceability plays a key role in building consumer trust by offering transparency throughout the entire meat production process. It gives consumers access to clear information about the origin of the meat, how it was processed, and the path it took to reach their plate. This openness helps reassure buyers about the quality and integrity of the product.
By minimizing risks such as food fraud and contamination, traceability systems provide peace of mind, ensuring the safety and dependability of the meat they purchase. Having insight into where and how their food is handled strengthens the trust and accountability shared between producers and consumers.
What new technologies are improving traceability in custom meat processing?
Modern Traceability Systems in Meat Processing
Traceability in meat processing has taken a leap forward with the help of advanced technologies, bringing greater transparency, safety, and efficiency to the industry. Take blockchain technology, for example – it’s being used to create secure, tamper-resistant records for every step in the supply chain. This ensures accountability at all stages, from the farm all the way to your dinner plate.
Another game-changer is the use of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and IoT (Internet of Things) devices. These tools enable real-time tracking of meat products, capturing detailed data about their journey. This not only simplifies operations but also reassures consumers about the quality and integrity of what they’re buying.
On top of that, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are stepping in to refine quality control processes. These technologies can identify potential problems early, ensuring that high standards are consistently met. By integrating these advancements, businesses are not just improving operations – they’re also building stronger trust with their customers.
Why do meat processors need to follow federal and state traceability rules?
Meat processors must adhere to federal and state traceability regulations to uphold food safety, comply with labeling and recall laws, and safeguard public health. These rules are crucial for identifying and swiftly removing contaminated products, which helps minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Traceability also plays a key role in preventing food fraud and strengthening consumer confidence by promoting transparency and accountability across the supply chain. By following these guidelines, processors show their dedication to providing safe, high-quality products while meeting legal requirements in the United States.

